Suggested Edit for Satellite
Suggested by PE0SAT on: 2022-02-01 11:07
Citation: CITATION NEEDED - https://xkcd.com/285/
Verdict: Approved
Reviewed by - on: 2022-02-01 12:18
| Name | RS-34 |
| NORAD ID | 39133 |
| Followed NORAD ID | - |
| Alternative Names | AIST-2 |
| Description | Aist is a Russian microsatellite developed by designed by a group of students, postgraduates and scientists of Samara Aerospace University in cooperation with TsSKB-Progress. The satellite measures the geomagnetic field, test the new small space vehicle bus, test methods to decrease microaccelerations to a minimum level and measure micrometeoroids of natural and artificial origin. The protoype unit was launched piggy back on the maiden flight of the Soyuz-2-1v Volga launch vehicle, while the first flight unit hitched a ride on a Soyuz-2-1a with the Bion-M 1 satellite. Source: https://space.skyrocket.de/doc_sdat/aist.htm |
| Owner/Operator | - |
| Status |
|
| Countries of Origin | |
| Website | - |
| Dashboard URL | - |
| Launch Date | - |
| Deploy Date | - |
| Image | 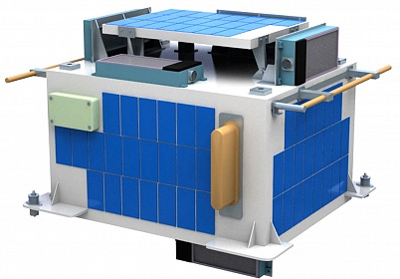 |
| Field | Previous | Suggested |
|---|---|---|
| Description | Aist 2D is a Russian microsatellite developed by designed by a group of students, postgraduates and scientists of Samara Aerospace University in cooperation with TsSKB-Progress. The satellite's mission is to test a new micro satellite bus. The prime payload is the Avrora imager which has a ground resolution of 1.48 meter in panchromatic mode and a 4.5 meter resolution in multispectral mode. Also on board is the BiRLK Bistatic P-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) capable of observing targets hidden by vegetation and subsurface features as well examination global geology and vegetation biomass. The DMS-01 mass spectrometer analyzes the gasseous environment of the satellite, especially the outgassing of the satellite components. | Aist is a Russian microsatellite developed by designed by a group of students, postgraduates and scientists of Samara Aerospace University in cooperation with TsSKB-Progress. The satellite measures the geomagnetic field, test the new small space vehicle bus, test methods to decrease microaccelerations to a minimum level and measure micrometeoroids of natural and artificial origin. The protoype unit was launched piggy back on the maiden flight of the Soyuz-2-1v Volga launch vehicle, while the first flight unit hitched a ride on a Soyuz-2-1a with the Bion-M 1 satellite. Source: https://space.skyrocket.de/doc_sdat/aist.htm |
| Image |

|

|